Core Cloud Technologies: Virtualization and its Role in Cloud Computing
Hi there. I am Philip Santus, a Web Programmer, developer, and writer. Today, I’m learning CLOUD COMPUTING. I’m a novice in this field but there is nothing I put my mind to that I can’t know.
Join me on this journey and let’s learn together.
As we know, with the increasing demand in the project, and requirements for different companies, we require new software along with different operating systems for applications, which creates more data and we need more processing power and more memory.
But there’s a way to overcome such situations known as virtualization. Hi guys, and welcome to another exciting lesson I learned. But before we begin, if you like reading tech articles, subscribe to any of the membership packages to never miss an update.
To understand what exactly virtualization is let’s take a look at an example. Meet John. He works as a software developer in an IT firm, and he often has to work on different projects involving multiple operating systems according to the requirements of the project, during which he often comes across cases where the managing of data becomes problematic due to the compatibility issues with the different operating systems, which makes it hard for the completion of the project. IMAGE DESCRIPTION BELOW:
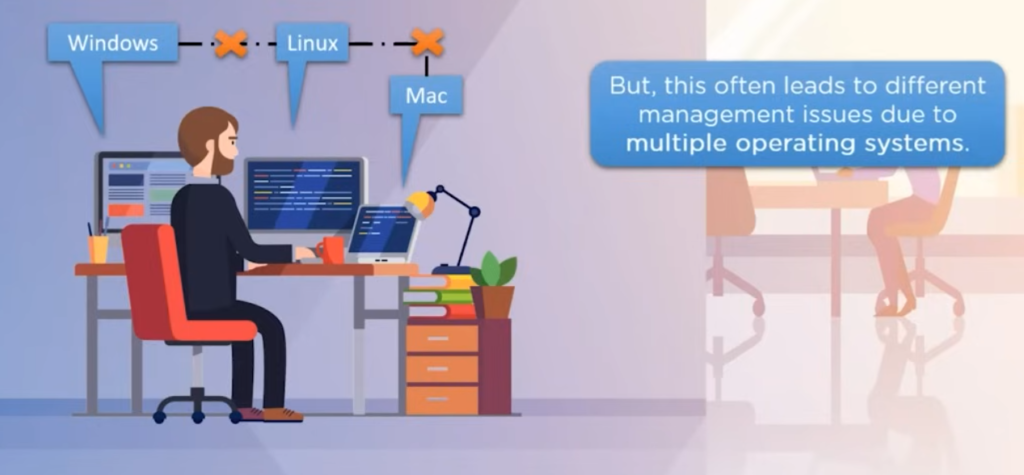

So what can John do to overcome such a problem? To overcome such a problem, he decided to use the way of virtualization.
But what is virtualization and how do they help us? Let’s take a look. To begin with, we’ll take a look at what exactly virtualization is and how it helps us. Then we’ll understand what virtual machines are. After that, we learn about the role and different types of hypervisor that are involved during the process of virtualization.
After that, we learn what different types of virtualization are available and how differently they affect our systems. And lastly, we will see what benefits virtualization provides us with. IMAGE DESCRIPTION BELOW:

Let’s begin with understanding what virtualization is.
(1). What Is Virtualization?

Virtualization is nothing but utilizing software to create a virtual layer over the hardware, which allows the system hardware to be used more efficiently and allows appropriate return for a hardware cost.
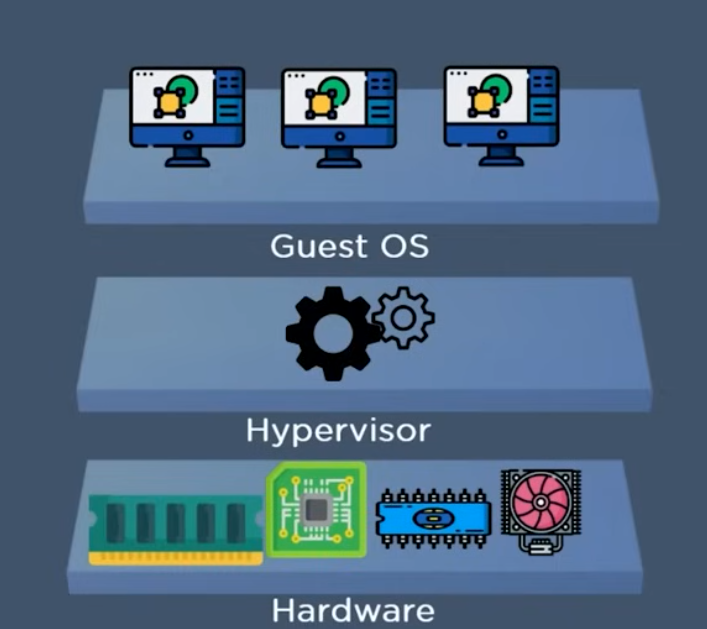
The software hypervisor also allows the elements of the system, like storage, memory, processor, etc, to be distributed among multiple separate and secure virtual computers known as virtual machines, to understand the situation of virtualization much better, let’s take a look at an example.
This is a system installed with the Windows operating system, which is officially known as the host OS, where the virtualization software, known as the hypervisor, will run.

And then, using the hypervisor software, we can have multiple instances of different OS, including Unix, Mac, and Linux, which are known as virtual systems, or guest OS.
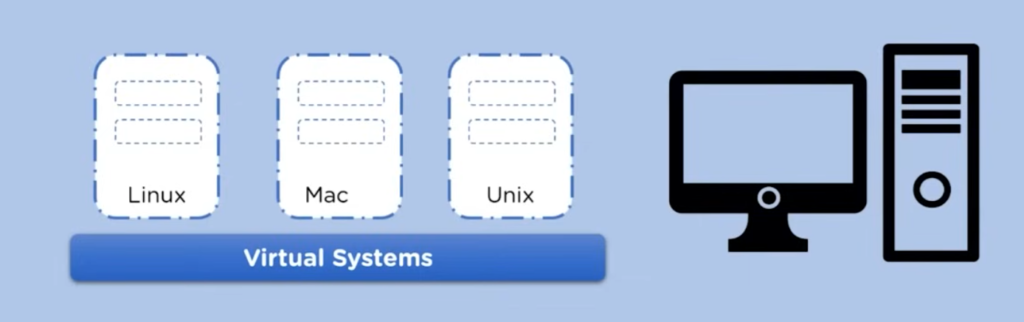
The working of the virtualization is only possible by using software known as a hypervisor. And later in the article, we will also learn about the working and different types of hypervisors involved.
What Is a Virtual Machine?

Now that we have understood what virtualization is, let’s take a look at what a virtual machine is, as the name suggests.
Virtualization is nothing but an emulation or a virtual representation of a physical operating system on a hardware device.
The virtual machines are also known as guest OS, whereas the physical system that they run on is also known as the host OS. IMAGE DESCRIPTION BELOW:

Now let’s take a look at the software that makes virtualization possible.
The Software That Makes Virtualization Possible(Hypervisor)
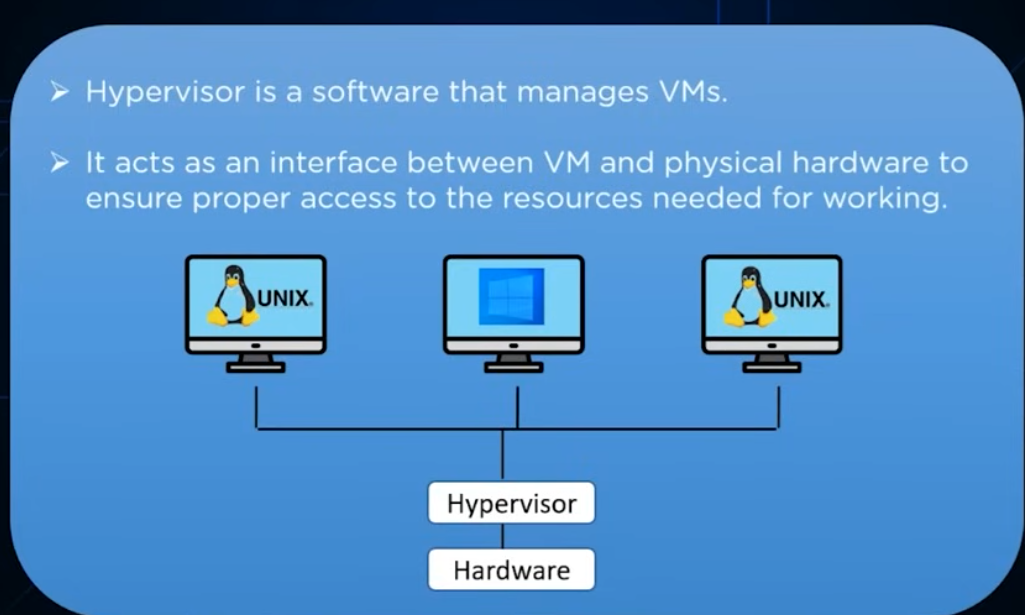
Hypervisor is a software layer that manages the virtual machines. It forms an interface between the physical system and the virtual machine, which ensures the proper access of the resources. It also manages the virtual machine so that they don’t interfere with each other resources.
Let’s take a look at what different types of hypervisors are there.
2). The Roles and Different Types Of Hypervisors

i) Type one or Bare metal hypervisor.
ii). Type Two Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitors.
Type One or Bare Metal Hypervisor:
The first type of hypervisor is known as the type one hypervisor, or the bare metal hypervisor. This type of hypervisor directly interacts with the hardware, system, and user resources.
Type Two Hypervisor or Virtual Machine Monitors:

The other type of hypervisor is known as the type two hypervisor, which runs an application on the host, and operating system, and the hypervisor also coordinates with the virtual machine for resource management.
Let’s take a proper look at the type one hypervisor. They run directly on top of the host operating system and utilize the hardware resources.
That is why they are also known as the bare metal hypervisor.
They take up the place of the host operating system and work as their operating system. Since this type of hypervisor works directly on the hardware system, they are highly efficient.
Now that we understand type one hypervisor, let’s take a proper look at the type two hypervisor. This type of hypervisor doesn’t directly work on the operating system hardware, but instead, it works as an application in the host operating system.
Where they are suitable for running individual systems. Users can also have different multiple OS installed in their physical system by using this type of hypervisor, due to the application-based working of the type two hypervisor. They are also known as virtual machine monitors, in short, VMMs.
Now that we understand what different types of hypervisor are, let’s take a look at what types of virtualization are present.
3). Different Types Of Virtualization Available:

i). Desktop Virtualization.
ii). Network Virtualization.
iii). Storage Virtualization.
iv). Application Virtualization.
The first type of virtualization is the desktop virtualization, then the network virtualization, storage virtualization, and lastly, the application virtualization.
The first type of virtualization is the desktop virtualization, then the network virtualization, storage virtualization, and lastly, the application virtualization.
Let’s take a look at them one by one.
i). Desktop Virtualization:
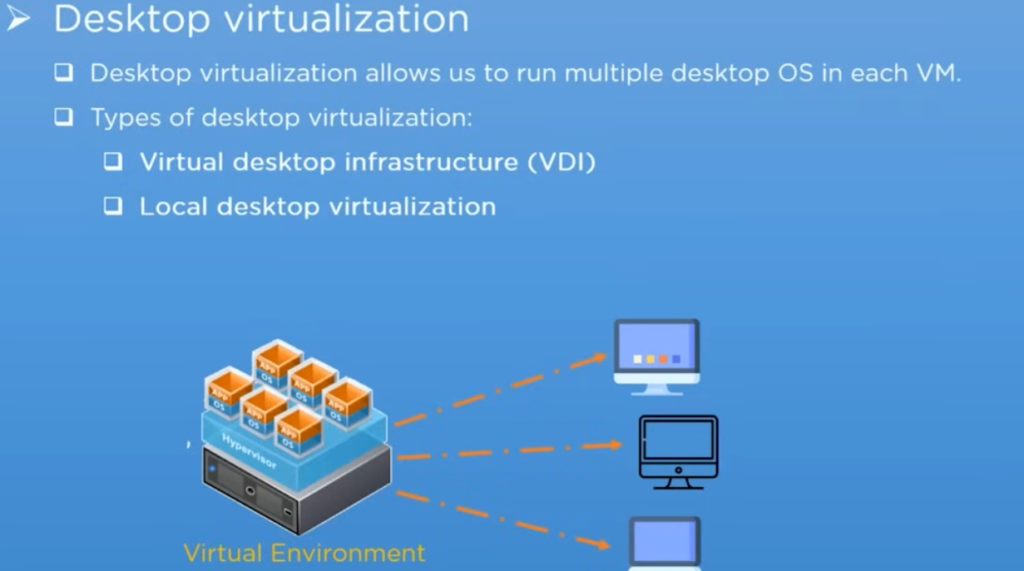
For desktop virtualization, as the name suggests, in this type of virtualization, we can run multiple operating systems on a single hardware system.
Let’s take a look at different types of desktop virtualization.
— VDI (virtual desktop infrastructure):
The first one is virtual desktop infrastructure and short VDI, which runs numerous virtual machines on a central server and then hosts the user according to the user’s requirements.
In this way, the user can access any operating system without having to physically install the particular operating system and its hardware system.
— Local Desktop Virtualization;
The second one is known as local desktop virtualization, as the name suggests. It uses hypervisor software on a local system which allows the user to run multiple operating systems simultaneously without having to affect the host operating system.
ii). Network Virtualization.
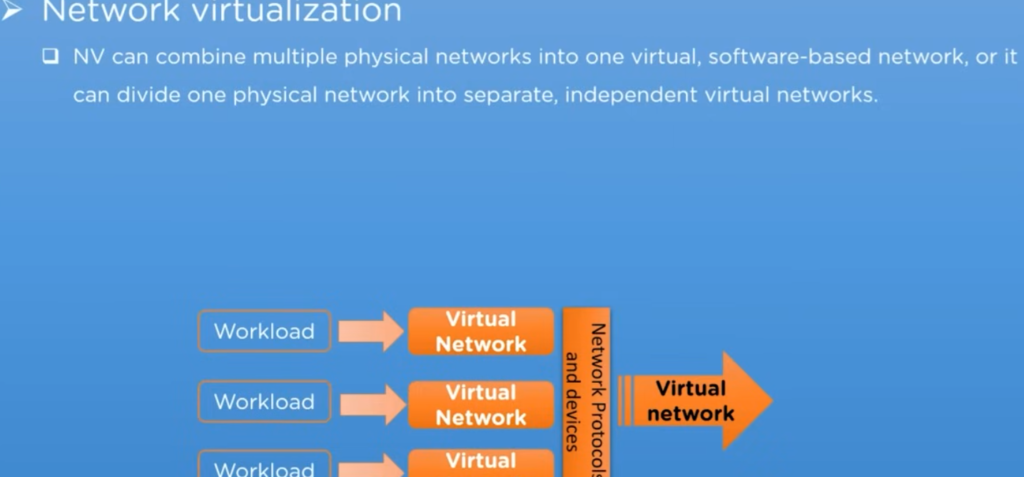
The next type of virtualization is the network virtualization. In this type of virtualization, the software creates a virtual instance of the network that can be used to manage from a single console, and it also forms the abstraction of the hardware components and functions, including switches, routers, etc, which simplifies the network management.
Types of Network Virtualization:
— Software Define Virtualization
— Network Function Virtualization
Different types of network virtualization are software-defined virtualization, which virtualizes the hardware that controls the network, graphing, and routing, and the other one is network function virtualization. Virtualizes the hardware appliances that provide network-specific functions easier to configure and manage. For example, firewall.
Let’s take a look at the third type of virtualization, known as storage virtualization.
iii). Storage Virtualization:
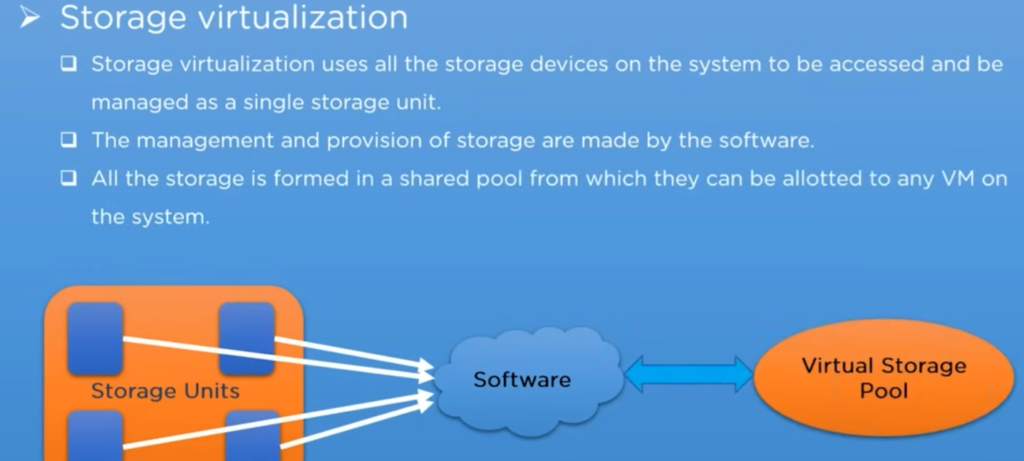
This virtualization enables all the storage devices on the system to be accessed and managed as a single storage unit.
The storage virtualization collects all the storage into a single pool from which they can allot to another virtual machine on the same network as required, and this makes it easier to assign storage for multiple virtual machines with maximum efficiency.
The last virtualization that we’ll discuss is the application virtualization.
iv). Application Virtualization:
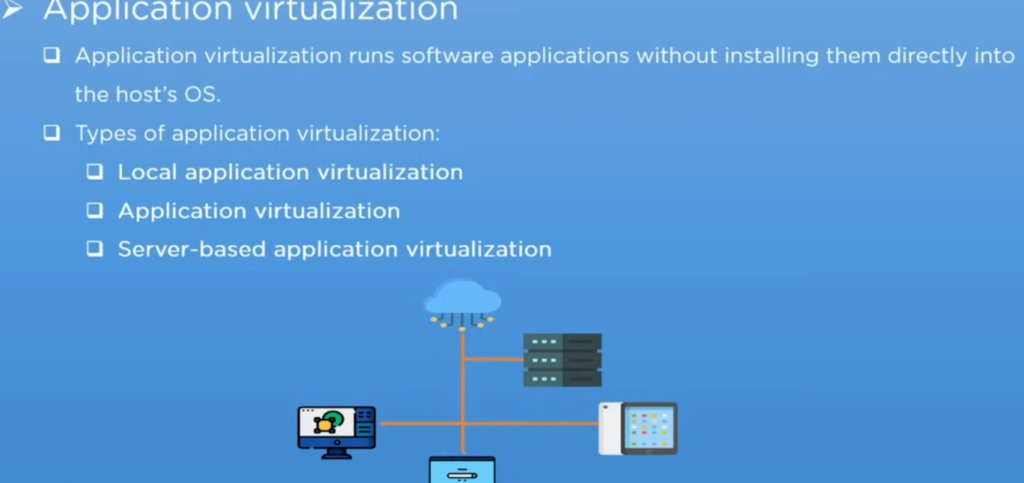
In this type of virtualization process, the application runs directly, without the need to install it into the system as it runs on a virtual environment.
Types of Application Virtualization:
— The Local Application Virtualization
— Application Virtualization
— Server Based Application Virtualization
The Local Application Virtualization;-
Different types of application virtualization are the local application virtualization. This type of application runs on the host device, but runs in a different virtual environment, but not in the hardware.
Application Virtualization:-
The second one is application virtualization. In this, the application is on the server side, and it sends some of the components to the host device according to the requirement.
Server Based Application Virtualization:-
And last is the server-based application virtualization, this application runs directly on the server side and sends only the interface to the client system.
Now let’s take a look at the benefits of virtualization.
4). The Benefits of Virtualization

RESOURCE EFFICIENCY:
The first one is resource efficiency, as the name suggests, before virtualization, each application server used its own hardware resources which were being underused, but with the having multiple virtual machines, maximum utilization of the hardware capacity occurs.
MINIMUM DOWNTOWN:

Then we have minimum downtime, which refers to the crashes of operating systems and applications, which can cause a halt in user productivity by using virtualization, the admin can run multiple similar virtual machines simultaneously, alongside and change over the working instances in case of a crash, instead of having multiple dedicated servers.
TIME MANAGEMENT:

Then we have the time management, by installing, and configuring a new system is not only costly, but also a waste of time.
In such a case, virtualization can solve the problem provided that the existing hardware resources are sufficient for running the virtualization software.
Otherwise, it can be configured for the same.
Now that we have reached the end of the module in which we learn what is virtualization? What is a virtual machine, and how to a hypervisor work during the process of virtualization, we can use this process to ease our work. If you have any doubts, you can ask them in the comment section. Thank you for reading.


One Comment