Cloud-Computing for Beginners: What is Cloud-Computing? — Cloud Computing Explained.
Hi there. I am Philip Santus, a Web Programmer, developer, and writer. Today, I’m learning CLOUD COMPUTING. I’m a novice in this field but there is nothing I put my mind to that I can’t know.
Join me on this journey and let’s learn together.
Let’s dive deep into the topics we’re going to discuss here, why we needed cloud computing, to begin with, and what are cloud computing and the different types of cloud computing available at the moment.
TABLE OF WHAT WE WILL DISCUSS
1). Why cloud computing?
2). What is cloud computing?
3). Types of cloud computing.
4). Cloud Providers.
5). Lifestyle of a cloud computing solution.
6). Cloud Computing with AWS.
We also are going to talk about the dominant cloud providers available in the market at the moment. We will touch on a few topics or scenarios on the life cycle of a cloud computing solution.
Let’s understand why cloud computing was needed. What was the problem that we had that cloud computing solved, and since then it has taken over the market?
Let’s understand that first, and that will solve a lot of unanswered questions about cloud computing or services that you might have.
1). Why Cloud Computing?

According to the image below,
here on the left, we have an owner of a business, and he wants to set up an easy or have IT infrastructure for his company. So he called Paul an IT-educated person in his company and consulted him about how to go about setting up an IT infrastructure.
Now, Paul is the kind of guy who keeps himself updated about what’s happening in the IT industry, and he frequently goes through learning about the recent technology.
So without missing a beat, Paul suggested, Why not set up the environment in the cloud? This is according to the image below.
However, his manager was not sure about the cloud and more than trying to understand what Cloud is, he was curious about the benefits of cloud over having a DC locally.
So Paul started to explain the very same thing I’m going to explain to you now. Let’s start with the expenditure or the billing model with the cloud.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ON-PREMISE AND CLOUD COMPUTING
The billing model is pay-as-you-go type meaning we use less and pay less, and we use more and we pay less per unit.
On the other hand, on-premises, we can’t expect that. We pay everything up front, and there is an additional operating cost, and it never lets us dynamically scale in on-premises, a lot of space is required for seating the servers, but in the cloud, no such space requirement is needed for the organization.
In on-premises, we also need a dedicated team to manage the hardware and software, but in the cloud, no such dedicated team is needed for most of the services.
They all get managed by the provider, and even if we need to manage them, the provider gives us options to manage them through the console, which is a lot, a lot simpler than managing directly from the device on the premises.
We need to admit the fact that data security is poor due to the cost involved in procuring the hardware and software to provide the security but in the cloud, the security standards are high due to the investments the providers have made to secure the data and to meet the compliance.
In traditional DC, there will generally be less focus on data recovery, and we kind of settle for less when it comes to data recovery, due to the cost involved, and you know the effort involved in replicating the data, and even if we set up a high performing data replication, a lot more can be done in the cloud for the same cost.
The on-premises environment lacks the flexibility needed today, if I need to restructure it for the New Age business needs, then the on-premises is not so friendly for such changes, but in the cloud, I can easily undo or tear down an environment or migrate to the new environment and tear down the old environment in few button clicks.
Now, looking at the number and the frequency of the releases that happen, scheduling updates would be a full-time job, but with the cloud, the updates happen automatically on-premises.
If I’m working with a team that is spread across the globe, working with them in unison and sharing the data is tedious work, but with the cloud, there are a lot of tools and technologies put together that make it easy to share the data with other members in the team or with the new prospective customer in on-premises.
If I’m working with a team that is spread across the globe, working with them in unison and sharing the data is tedious work, but with a cloud, there are a lot of tools and technologies put together that make it easy to share the data with other members in the team or with a new prospect customer I will be working with who is present across the other side of the globe, in on-premises, the data will be present inside the DC or the on-premises DC, and even a valid user trying to access the data from outside the organization is a tough task, but with a cloud, as long as someone has internet providing the person access is just a few mice clicks away.
Talk about implementation building an on-premises D. DC takes time. But with the cloud, we can bring our DC into the cloud within weeks.
BELOW IS THE GRAPHIC EXPLANATION OF ON-PREMISES Vs CLOUD COMPUTING
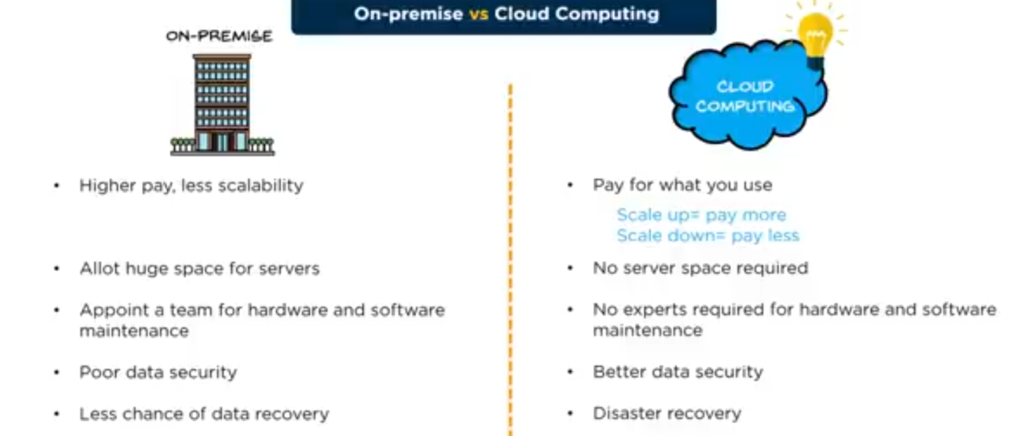

After all this explanation and comparisons and talking about benefits, Paul’s manager was fully enlightened and wanted to have his IT environment in the cloud.
But our Paul is not done yet, and he took his manager through another level of discussion about the cloud, just like I’m going to take you now.
2). So let’s talk about what is cloud computing.

Now, cloud computing is the ability to deliver on-demand computing service over the internet, and that too, on a pay-as-you-go basis.

Now you might think, Well, what does that mean? Let me explain how, with Cloud rather than managing files on local storage devices, cloud computing makes it possible to save them over the internet and access them from the internet.
So I can be a mobile person, and I’m moving from place to place, but I can access the storage from the internet because it’s on the internet, and if I want to give access to somebody else, again, it’s easy for me to give access to them, as long as they have an internet connection available with them.
Now let’s move further and talk about or get an understanding of the types of cloud computing.
3). Types of Cloud Computing:

We can categorize the different types of cloud computing based on two wide categories,
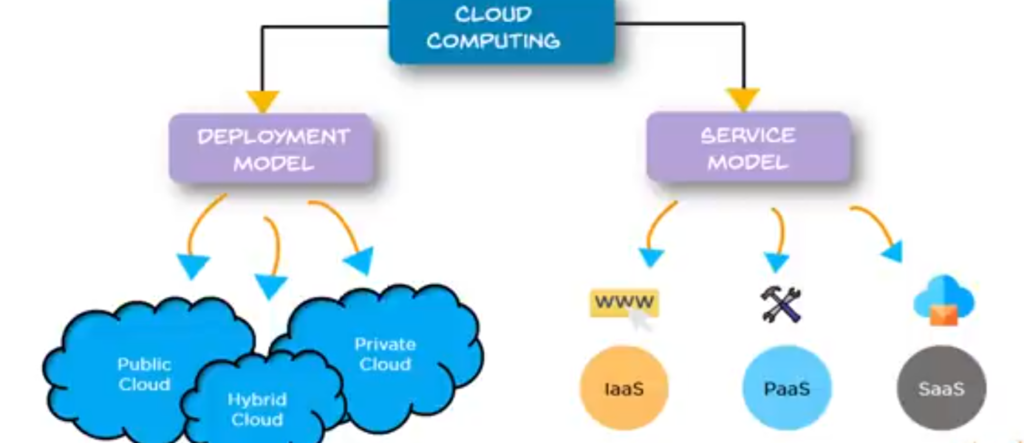
a). One is the deployment model and
b). The other is the service model.
Let’s talk about the deployment model.
The deployment model:
The first deployment model is categorized into three types.
a). Public,
b). Private,
c). hybrid cloud.
In other words, public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud.
It’ll be easy for me to explain, and also it’ll be easy for you to understand if I walk you through this example, considering the different types of vehicles we use to commute from one place to another.
For example, if I want to travel, I can pick a bus that is accessible to anyone I get in, and I pay for the seat that I occupy, and I pay for the time that I will be traveling in it and I’m done.
The cost is very low. Here, a similar kind of thing happens in the public cloud. I pay only for the resources that I use, and I pay for how long I use them. If I use less, I pay less. If I use more, I pay more for that month.
Simple, on the other hand, private cloud is like buying your car and using it for commuting purposes. Here, I pay a huge amount upfront, and it is all owned only by me. I do not pay for it in an hourly fashion, but completely and all upfront. The cost here is very high.
Thirdly, if I want the best of both types, like the comfort of my car, and still don’t want to pay all upfront. Otherwise, I only pay for the time that I use the service. I can rent a car.
Similarly, I can have it in a hybrid environment, meaning, if I already have a DC, I can integrate it with the cloud and use both the DCS, and that would become a hybrid environment. Alright, so that was good and learning.
GRAPHIC INTERPRETATION OF DEPLOYMENT MODEL
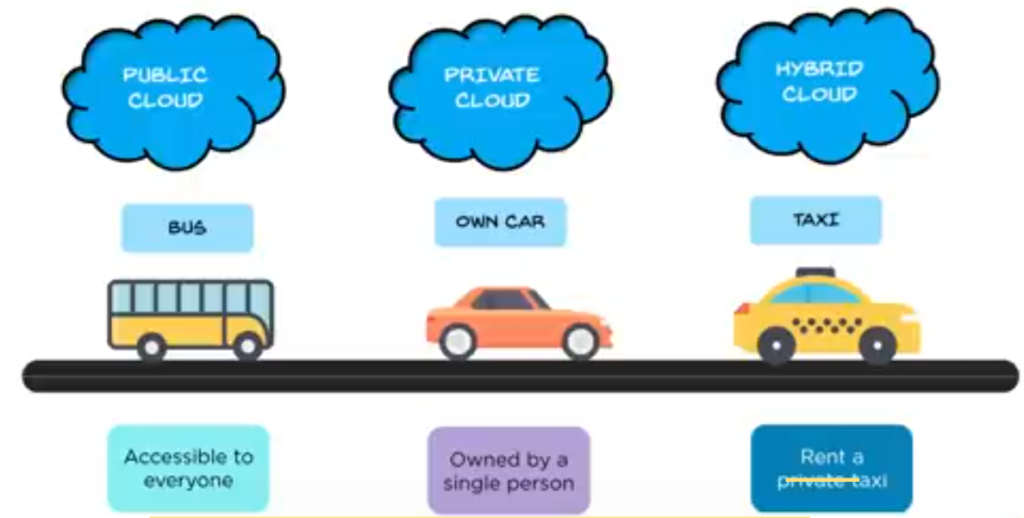
Let’s summarize the types of cloud-based deployment models, and what we know now about the public cloud.
Public Cloud is a cloud infrastructure that’s made available to the general public over the internet, and it is owned by the cloud provider.
Some of the major players as cloud providers are AWS, Microsoft, Azure, IBM’s Blue Cloud, Suncloud, and private cloud. Now this cloud infrastructure is exclusively operated by a single organization. It can be managed by organizations or third parties and may exist on-premises or off-premises. Doesn’t matter.
But the point here is that this is exclusively operated for a single organization, and some companies that provide private cloud are AWS and VMware and hybrid cloud is the best of both public and private cloud.
For example, federal agencies, opt for private clouds for storing and developing personal data, and they use public clouds to share non-sensitive data with the general public or with other government departments.
Now let’s talk about different clouds based on the service model.
The Service Model:
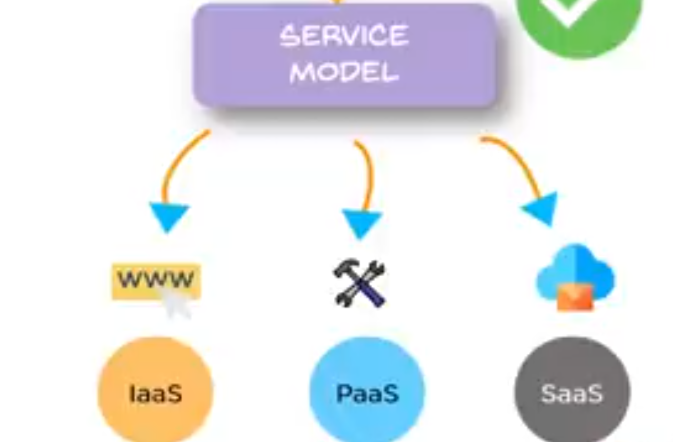
If we need to categorize them broadly, we can categorize them as Infrastructure as a Service, IAS or platform as a service, PaaS or software as a service, SAS, sometimes referred to as PaaS and SaaS.
Now at this moment, you could be like this guy, thinking, Sam, I thought you’re done categorizing the cloud. Now you’re going to talk about three more categories.
Which one should I pick? Well, let me explain. If all that you want is just a VM and you have all the expertise to install the software on top of it and make it work.
Then go for it if you only want a platform or an interface to program or an interface to upload a program and make it run. Then pick PaaS, or if all that you want is a finished product hosted in the cloud and able to access it through the internet, then go for SaaS.

Here you get a username. Password for an application, and you can begin to customize the application based on your needs. All right, let’s talk about IaaS in a bit more detail.
IaaS

IaaS gives basic computing infra. It’s based on a pay-for-what-you-use model, and some of the cloud providers who are big players are AWS, Azure, and Google.
Here the users generally will be IT admins.
PaaS:

In PaaS, the provider gives you a platform or a runtime environment for developing, testing, and managing applications. It’s platform-ready.
You buy the platform, you upload your code, and you start working on it, and it allows the software developers to deploy applications without running the underlying infrastructure.
As you might have guessed by now, the interesting candidates who would use PaaS are software developers.
SaaS:

And in SaaS, everything is managed by the vendor, be it the hardware or the software. It’s managed by the vendor.
And we pay for the service. And we pay for it through a pay-as-you-go, subscription model. And as you might have guessed, the end users here would be the end customer itself.
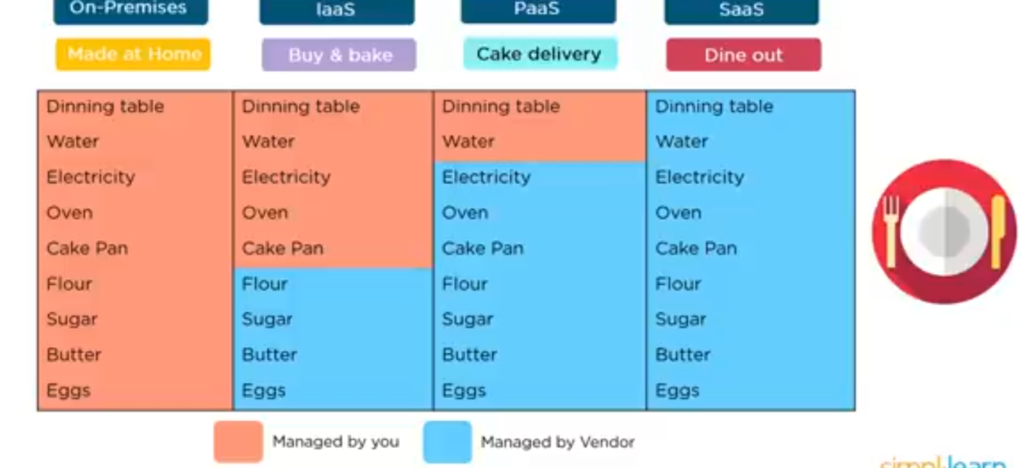
Alright, let’s put together everything on the same page and compare and contrast the different types of service models in this chart. It explains the difference between the full models, starting from on-premises to IaaS and then PaaS and SaaS.
THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
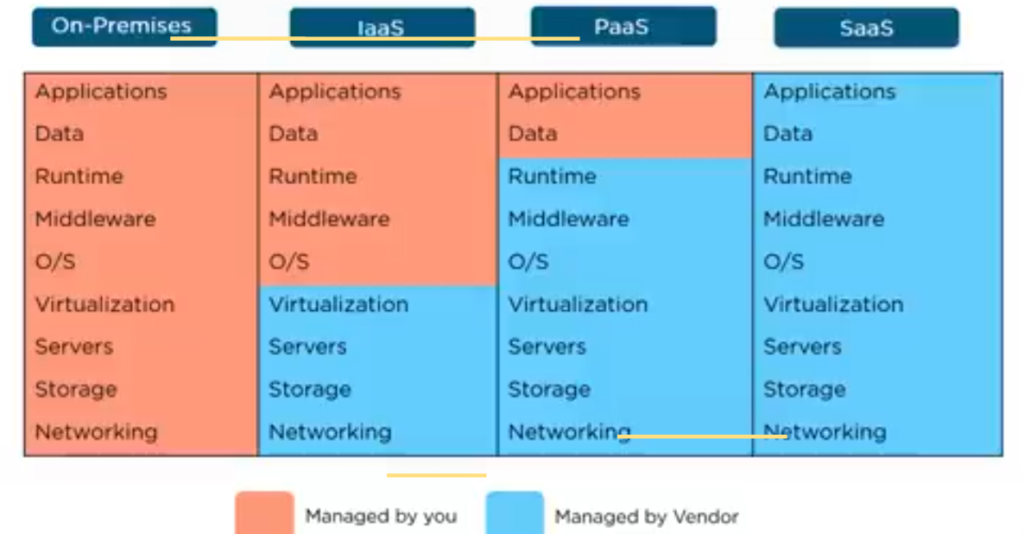
It is self-explanatory that the resources managed by us are huge on-premises, and little less in IaaS and further less or reduced in PaaS, and nothing to manage when it comes to SaaS.
Let me also explain the different types of cloud services through an example like this.
Let’s say that you have a crush on cake and you’re planning to bake one yourself.
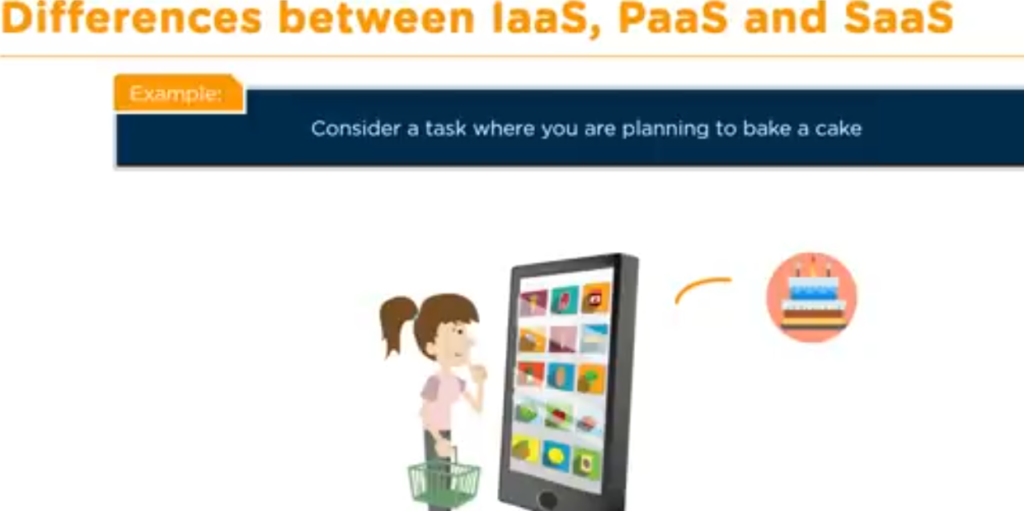
Now let’s look at the options you can have. You can make all the ingredients yourself be the floor, butter and, you know, put together and bake the whole thing yourself using your oven, pan, you know, the needed water and the rest, you get an idea, right? Everything is yours, and that’s on the premises.
All that you use is owned by you, and nothing is managed by the vendor. Image illustration below:
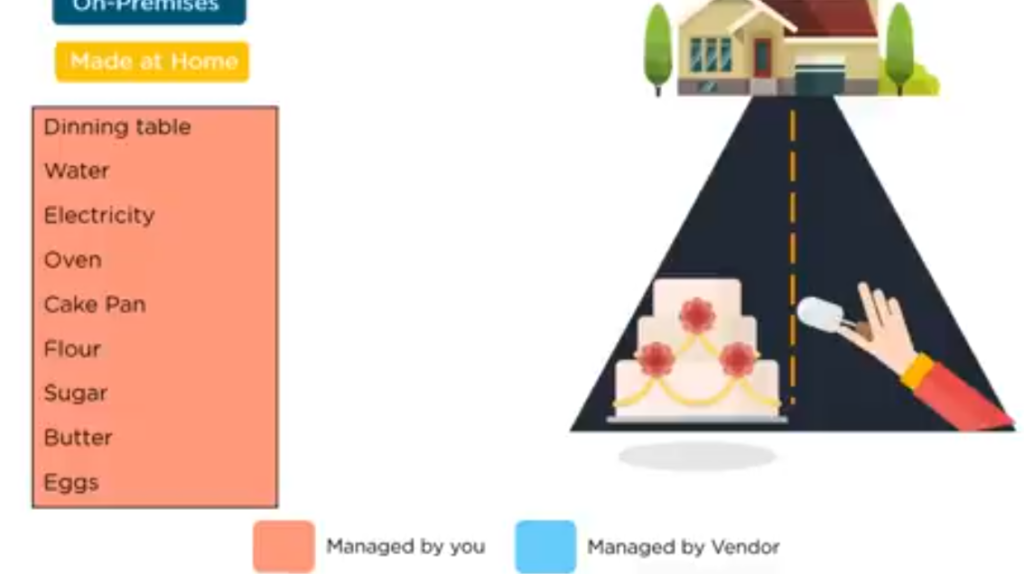
The other option you can have is to buy the ingredients and mix and bake the cake yourself.
Now this would be like IaaS here, the infra is managed by the provider, and we get to use it and customize it the way we want it.
Here, the cloud service is then shared responsibility.
Image description below:
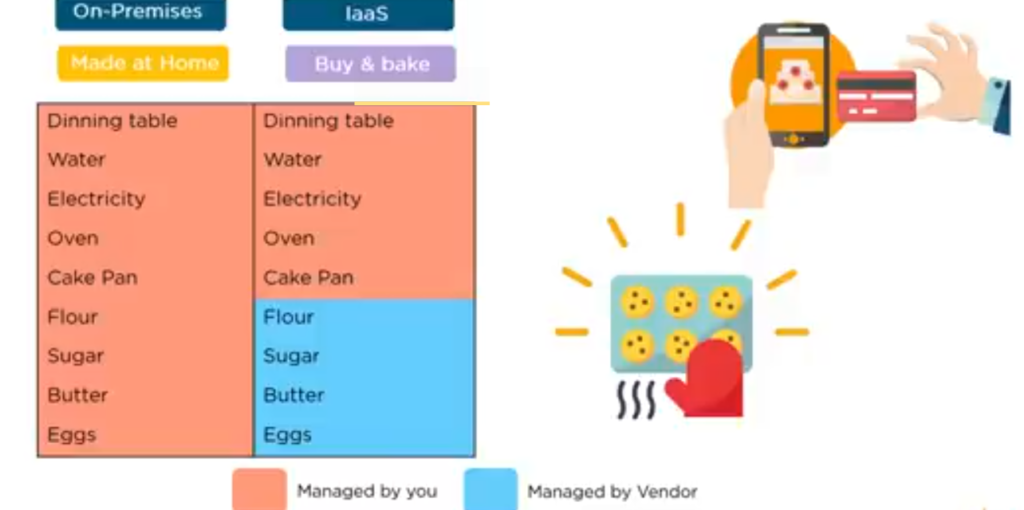
The other option you still have on hand is simply to pick up a phone and order a cake. Now this is a lot simpler than the rest we discussed so far.
You know, it’s simply picking up the phone and ordering the cake and paying for it when it arrives, simple and when it reaches home, you will have to arrange the table, garnish the cake, if that’s needed, and then enjoy the cake.
Image description below:
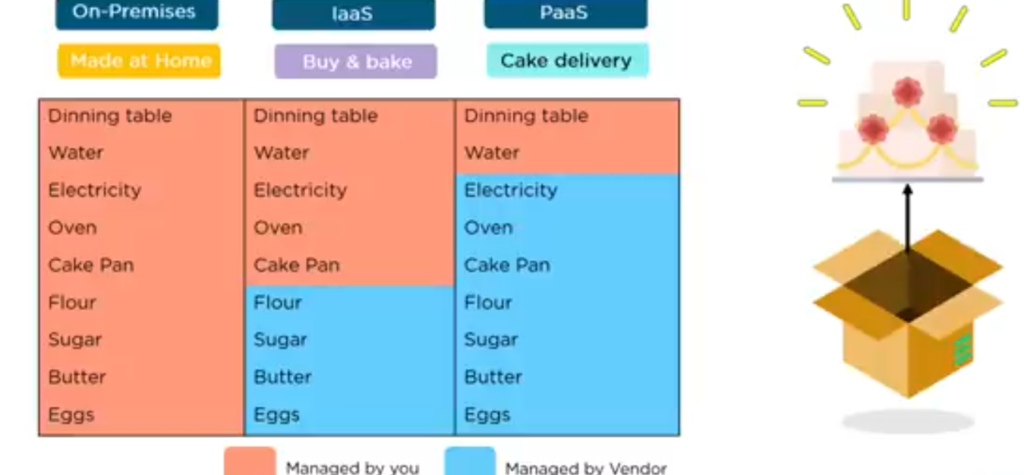
It’s the same way with pass just get the platform in which you would run your code upload your code and start running your application. Here you and the vendor still share the responsibility.
You still have one more option left, which is simply to go out and dine. This is a lot, a lot simpler, that it requires no effort from us at all. You buy the fully finished and garnished cake pay for it and walk out with no responsibility for making the cake.
It’s the same way with SaaS. We buy the finished product and pay for the finished application. Image description below:
Next thing, let’s talk about the different cloud providers, Amazon Web Services.
4). Cloud Providers.

a). AWS is a cloud computing service provided by Amazon. It provides a mix of infrastructure as a service. IaaS platform as a service, PaaS, and package software as a service, called SaaS offerings.
b). Microsoft Azure, formerly known as Windows, Azure is a cloud computing service by Microsoft, and it sort of specializes in using Cloud for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications through the service throughout the global network that Microsoft manages.
It also provides software as a service, platform, and infrastructure as a service, and it supports lots of different programming languages tools, and frameworks, including both Microsoft and third-party software and systems.
c). IBM Cloud is a cloud computing service offered by IBM. IBM Cloud includes Infrastructure as a Service, Software as a Service, and Platform as a Service. Now the difference is here, it offers public, private, and hybrid cloud delivery models.
d). VMware, on the other hand, is a subsidiary of Dell Technologies and provides cloud computing and platform virtualization software and services.
It was the first commercially successful company to virtualize the x86 architecture.
e). Google Cloud Platform, on the other hand, is offered by Google. It’s a suit of cloud computing services that run on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end user, products such as the Google search and the YouTube you’re familiar with, alongside a set of managed tools, it also provides cloud services, including computing services, data storage services, data analytics, and machine learning services.
f). Digital Ocean, on the other hand, is a headquarter. In New York City, with data centers worldwide, Digital Ocean provides developers with cloud services that help to deploy and scale applications that run simultaneously on multiple computers.
As of January 2018, Digital Ocean was the third-largest hosting company in the world in terms of web-facing computers.
GRAPHIC ILLUSTRATION OF VARIOUS CLOUD PROVIDERS
CLOUD COMPUTING IN AWS, AND AMAZON WEB SERVICES

Let’s talk about cloud computing in AWS, and Amazon Web Services. AWS is a cloud computing service provided by Amazon, and these services are accessible over the internet because AWS provides infrastructure as a service, it’s a flagship offering, and we can create and deploy any type of application in the cloud on top of the IaaS that Amazon provides and you know, the best part here is the subscriptions are Pay As You Go type, you use less and pay less and only for what you have used.
You use more and pay more, but still less per unit for the service used. Attractive, isn’t it?
5). Lifestyle of a cloud computing solution.
Now, let’s talk about the life cycle of the cloud computing solution, the very first thing in the life cycle of a solution, or a cloud solution, is to get a proper understanding of the requirements.
I didn’t say, to get the requirement, but said, to get a proper understanding of the requirement. It is very vital because only then we will be able to properly pick the right service offered by the provider.
Getting a sound understanding. The next thing would be to define the hardware, meaning choose the compute servers that will provide the right support, where you can resize the compute capacity in the cloud to run application programs.
Getting a sound understanding of the requirements helps in picking the right hardware. One size does not fit all. There are different services and hardware for different needs you might have, like EC two if you’re looking for IaaS, lambda if you’re looking for serverless computing, and ECS that provides containerized service.
So there are a lot of hardware available. Pick the right hardware that suits your requirements. The third thing is to define the storage.
Choose the appropriate storage service where you can back up your data and a separate storage service where you can archive your data locally within the cloud or from the internet and choose the appropriate storage.
There is one separately for backup called s3 and there is one separately for archival that’s for glaciers. So you know, knowing the difference between them helps in picking the right service for the right kind of need.
Define the network, define the network that securely delivers data, video, and applications, and define and identify the network services properly.
For example, VPC for network route 53 for DNS and direct connection for private P to P line from your office to the AWS data center set up the right security services, Iam for authentication and authorization, and KMS for data encryption at rest.
So there are a variety of security products available. We have to pick the right one that suits our needs, and there are a variety of deployment automation and monitoring tools that you can pick from for example, cloud watch is for monitoring.
Auto Scaling is for being elastic, and cloud formation defines the management process and tools. You can have complete control of your cloud environment if you define the management tools that monitor your AWS resources and or the custom applications running on the AWS platform.
There is a variety of deployment automation and monitoring tools you can pick from like Cloud Watch for monitoring, auto-scaling for automation, and cloud formation for deployment.
So knowing them will help you define the life cycle of the cloud computing solution properly similarly, there are a lot of tools for testing a process, like code star code build and code pipeline.
These are tools with which you can build, test, and deploy your code quickly.
Finally, once everything is set and done, pick the analytics service for analyzing and visualizing the data using the analytics services where we can start querying the data instantly and get a result.
Now, if you want to visually view the happenings in your environment, you can pick Athena, and other tools for analytics are EMR which is elastic, MapReduce, and Cloud Search.
So what did we learn? We learned about what is cloud computing. Understood the basics of cloud computing.
We understood the types of cloud computing based on deployment models and service models.
And then we understood how cloud computing is with AWS. Now, how AWS is a cloud computing service provider, and the benefits of using AWS over other providers.
Finally, we also looked at the life cycle of the cloud computing solution. I hope you enjoy this lesson. I’ll meet you in the next lesson. Thank you.


One Comment